Semisolid dosage forms are mainly meant for external application e.g. ointments, creams, jellies and pastes etc. The suppositories are also included in this category although these are unit dosage form.
OINTMENTS
Ointments are semi-solid preparations meant for external application to the skin or mucous membrane. They usually contain a medicament medicaments dissolved, suspended or emulsified in an ointment base, They may contain a suitable antimicrobial preservative. The ointments are mainly used as protective or emollient for the skin.

Classification of Ointments
Ointments may be classified as follows:—
(l) According to their therapeutic properties based on penetration
(2) According to their therapeutic uses
Ointment classified according to properties based on penetration
(i) Epidermic ointments : These ointments are meant for action on epidermis and produce local effect. They are not absorbed. These types of ointments are mainly used as protectives, antiseptics, local anti-infectives and parasiticides.

(ii) Endodermic ointments : These ointments are meant for action
on deeper layers of cutaneous tissues. They are partially absorbed and act as emollients, stimulants and local irritants.
(iii) Diadermic ointments : These ointments are meant for deep penetration and release the medicaments that pass through the skin and produce systemic effects.
Ointments classified according to therapeutic uses
(i) Antibiotic ointments : These ointments used are used to kill, microorganisms. E.g neomycin
bacitracin, chlorotetracycline etc.
(ii) Antifungal ointments : These ointments are used to inhibit or kill the fungi. The commonly used antifungal agents are benzoic acid, salicylic acid and nystatin etc.
(iii) Anti-inflammatory ointments : These ointments are used to relieve inflammatory, allergic and pruritic conditions of the skin. Betamethasone valerate, hydrocortisone and its acetate are some of the commonly used anti-inflammatory agents.
(Vi) Antipruritic ointments : These ointments are used to relieve itching. The antipruritic drugs commonly used are benzocaine and coal tar.

(v) Astringent ointments : These ointments causes contraction of the skin and decrease discharges. The astringents commonly mixed with ointment bases are calamine, zinc oxide, acetic acid and tannic acid.
(vi) Antieczematous ointments : These ointments are used to prevent oozing and excretion from vesicles on the skin. The drugs which are commonly mixed with ointment bases are hydrocortisones, ichthammol, coal tar and salicylic acid.
(vii) Keratolytic ointments : These ointments are used to remove or soften the horny layer of the skin. The drugs that remove keratin are resorcinol, salicylic acid and sulphur.

(viii) Counter-irritant ointments : These ointments are applied locally to irritate the skin, thus reducing or relieving another irritation or deep seated pain. The drugs used are capsicum, methyl cellulose, oleoresin and iodine.
(ix) Ointments used for dandruff treatment : These ointments are applied locally to get relief from dandruff. The drugs commonly used are salicylic acid and cetrimide.
(x) Ointments for psoriasis treatment : Coal tar, corticosteroid, dithranol and salicylic acid are incorporated with the suitable ointment base for the treatment of psoriasis.
(xi) Parasiticide ointments : These ointments destroy or inhibit living infestation, such as lice and ticks, The drugs commonly mixed with ointment bases are benzyl benzoate, hexachloride, sulphur etc.
(xii) Protectant ointments : These ointments protect the skin from moisture, air, sun rays or other substances such as soaps or chemicals. The drugs which are used in protectant ointments are calamine, zinc oxide, silicones, titanium dioxide etc.
Ointment Bases
The ointment base is that substance or part of an ointment, which serves as carrier or vehicle for the medicament. While selecting a suitable ointment base, the factors such as the action desire, nature of the medicament to be incorporated and the stability of an ointment are to be considered.
An ideal ointment base should possess the following properties:—
(i) It should be inert, odourless and smooth.
(ii) It should be physically and chemically stable.
(iii) It should be compatible with the skin and with the incorporated medicaments.
(iv) It should be of such a consistency that it spreads and softens when applied to the skin with stress.
(v) It should not retard healing of the wound.
(vi) It should not produce irritation or sensitisation of the skin,
There is no single ointment base which possesses all the qualities Of an ideal ointment base. So it becomes necessary to use more than one ointment base in the preparation of ointments.
Classification of Ointment Bases
l. Oleaginous bases
2. Absorption bases
3. Emulsion bases
4. Water soluble bases
1. Oleaginous Bases : These bases consist of water insolubl hydrocarbons, vegetable oils, animal fats and waxes. The Constituents hydrocarbon bases are soft paraffin, hard paraffin and liquid paraffin
(i) Petrolatum (soft paraffin) : It is a purified mixture of solid hydrocarbons obtained from petroleum. There are two varieties of soft paraffin, one is yellow soft paraffin and other is white soft paraffin White soft paraffin is prepared by bleaching yellow paraffin. Both these soft paraffin have melting point of 38 0C to 56 0C. White soft paraffin is used when the medicament is white or colourless. White soft paraffin is never used in the preparation of ophthalmic ointments because the white soft paraffin may contain small traces of bleaching agent which are generally left over after bleaching the yellow paraffin. Hence, the white soft paraffin may cause irritation to the eye.
ii)Hard paraffin : It is a purified mixture of solid hydrocarbons from petrolatum. It is colourless or white translucent, Odourless, tasteless wax like substance. It is used to harden or soften the ointment base.
(iii) Liquid paraffin : It consists of a mixture of liquid hydrocarbon and obtained from petroleum by distillation. It is also known as white mineral Oil or liquid petroleum. It is a colourless, odourless, tasteless and transparent oily liquid. It is soluble in ether and chloroform but insoluble in water and alcohol. It is used along with hard paraffin and soft paraffin to get a desired consistency of the ointment.
The oleaginous bases are losing their importance nowadays for the following reasons•.—
i)They are greasy.
ii)They are sticky and are difficult to remove both from skin and clothing.
iii)They retain body heat which may produce an uncomfortable feeling of warmth.
iv)They do not help in the absorption of medicaments.
(v) They prevent drainage on oozing areas and also prevent evaporation of cutaneous secretions along with perspiration.
2. Absorption Bases : These bases are generally anhydrous substances which Ivave the property of absorbing (emulsifying) considerable quantities of water but still retaining their ointment-like consistency. The absorption bases are of two types:—
(i) Non-emulsified bases (ii) Water in oil emulsions
The non-emulsified bases absorb water and aqueous solutions producing w/o etnulsions e.g., wool fat, wool alcohol, beeswax and cholesterol. The water in oil emulsions are capable of absorbing more water and Ivave the properties of non-emulsified bases e.g., hydrous wool fat (lanolin).
(i) Wool fat : It is the purified fat-like substance obtained fronl the wool of sheep. It is also known as anhydrous lanolin. It can absorb about 50% of its weight of water. So it is used in ointments where the PVOportion of water or aqueous liquids to be incorporated in hydrocarbon base is too large. It is an important constituent of situple ointnwnt base and eye ointment base.
Hydrous wool fat : It is the purified fat like substance Obtained from wool of sheep. It is also known as lanolin. It is insoluble in water but soluble in ether and chloroform. Hydrous wool fat is a mixture of 70% w/w wool fat and 30% w/w purified water. It is used alone as emollient and as an ingredient of several other ointments.
Wool alcohol : It is obtained from wool fat by treating it with alkali and separating the fraction containing cholesterol and other alcohols. It contains not less than 30% of cholesterol. It is used as an emulsifying agent for the preparation of w/o emulsion. It is also used to improve the texture, stability and emollient properties of o/w emulsions.
Beeswax : It is purified wax obtained from honey comb of bees. It is available as yellow beeswax and white beeswax. White beeswax is obtained by bleaching the yellow beeswax. It is used as a stiffening agent in pastes and ointments.
These bases have following advantages
( l ) These bases are compatible with large number of medicament;
These bases can absorb a large quantity of water or aqueoug substances.
These bases are relativelv heat stable.
These bases may be used in their anhydrous form or in emulsified form.
These bases are quite greasy, but these can be easily removed from the skin as compared to oleaginous bases.
3. Emulsion Bases : These bases are semisolid or have a creamlike consistency. Both o/w and w/o emulsions are used as ointment base. The oil in water type of emulsion bases are more popular because these can be easily removed from the skin or clothes by washing with water. The w/o type of bases are greasy and sticky. The emulsifying ointment is prepared from emulsifying wax, white soft paraffin and liquid paraffin.
4. Soluble Bases : These are commonly known as less ointment bases”. The water-soluble bases consist of water soluble ingredients, such as, polyethylene glycol polymers which are POPU1arly known as “carbowaxes”. The carbowaxes are water soluble, non-volatile and inert substances. Depending upon the molecular weight, carbowaxes are available in different consistencies i.e., liquids, semisolids and solids. Their molecular weight varies from 200 to 8000. By mixing different carbowaxes, ointments of varying consistencies can be obtained.
Tragacanth, gelatin, pectin, cellulose derivatives, bcntonite magnesium – aluminium silicate and sodium alginate are also used as water soluble bases.
SELECTION OF DERMATOLOGICAL VEHICLES
There are large number of ointment bases which are available in the Inarket. These have already been discussed. But non of the above discussed ointment base, fulfils all the requirements of an ideal ointment base. Following are the factors which govern the selection of an ideal base for ointments:—
(A) Dermatological factors (B) Pharmaceutical factors
(A) Dermatological Factors
1. Absorption and penetration : Absorption means actual entry into blood stream i.e., systemic absorption, whereas “penetration” indicates passage through the skin i.e., cutaneous absorption.
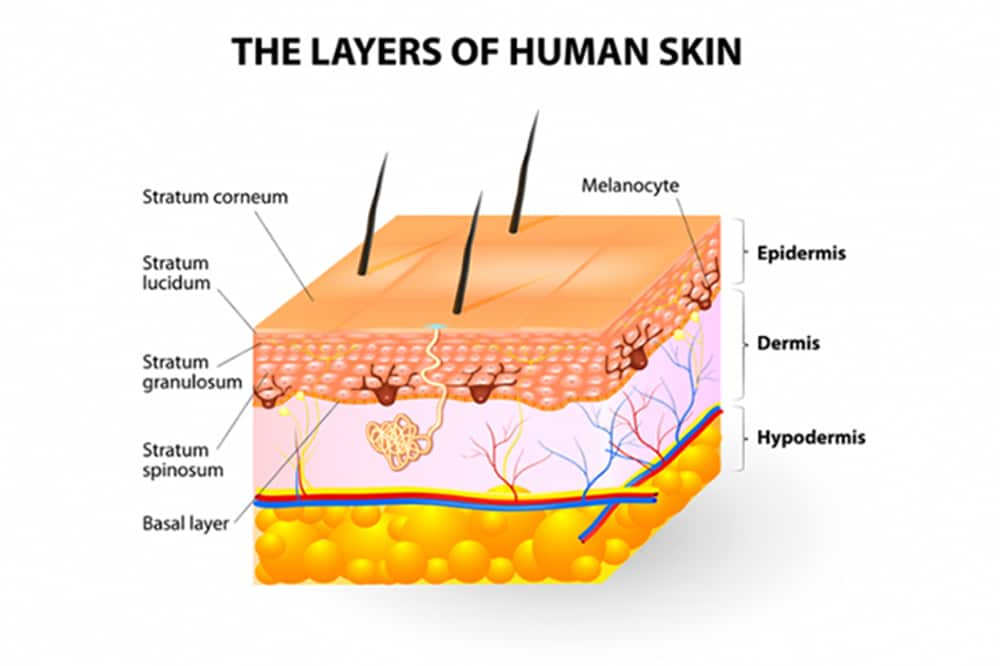
The skin has three main layers, the epidermis, dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis is non-vascular and is entirely cellular. The ointment base penetrates deep into tissues of the skin along with the medicament and which in turn allows the systemic absorption of medicament into the blood stream.
It is proved scientifically that animal fats (lard and wool fat) and fixed oils penetrate more readily through the skin in comparison to oils (paraffin). The substances which are soluble both in oil and water are Inost readily absorbed. The o/w emulsion bases release the medicament more readily than oleaginous bases or w/o emulsion bases.
Effect on skin function : Greasy bases may interfere with the skin function like heat radiation and sweat excretion. Moreover, they are irritant to the skin. The water soluble bases and o/w emulsion bases provides a cooling effect rather than the healing effect. These bases mix readily with skin secretions.
Miscibility with skin secretions and serum : Skin secretions are more readily miscible with emulsion bases as compared to greasy bases. Hence drug is more rapidly and completely released to the skin. Due to this reason lesser proportion of the medicament is needed when emulsion bases are used. Similarly, o/w emulsion bases being readily miscible with scrum from broken skin are very useful as an ointment basc for ointments meant for weeping eczema.
Compatibility with skin secretions : Generally neutral ointment bases are preferable because they do not cause discomfort in use and are compatible with majority of medicaments. The ointment bases should have a pH around 5.5 which is the average pH of the skin secretions.
Freedom from irritant effect : The ointment bases used should be non-irritant. Greasy bases cause irritation and may cause oedema. All bases used should be of high standard of purity and bases used in preparing eye ointments should be non-irritating and free from foreign particles.
Emollient properties : Under normal conditions, continuous hydration occurs which keeps the skin sufficiently moist. Dryness and brittleness of the skin cause discomfort to the skin. Therefore, the ointment bases used should possess emollient properties that should be able to keep the skin moist. The humectants like glycerin and propylene glycol keep the skin surface moist and soft. Wool fat, lard and paraffin keep the skin soft by preventing rapid loss of moisture from the skin.
Ease of application and removal : The ointment bases used should be easily applicable and at the same time they are easy to be removed from the skin. Stiff and sticky ointment bases are not suitable because they may cause damage to the newly formed tissues of the skin. Due to this reason the emulsion bases are preferable as they are softer and spread more readily over the area to which they are applied. The emulsions particularly o/w type are easily removable with water.
(B) Pharmaceutical Factors
Stability : The fats and oils obtained from animal and sources are liable to undergo oxidation. This can be prevented b incorporating a suitable antioxidant in desired concentration in the ment base. O/w type emulsion bases are liable to microbial growth and needs a proper preservative. Similarly ointments containing liquid fin may get oxidised on perlong storage. Emulsified bases are liable to phase separation due to improper formulation or under the influence of temperature.
Solvent properties : Most of the medicaments used in the preparation of ointments are generally insoluble in the ointment bases. Hence, for the uniform distribution, it is necessary to mix finely powdered drug in the ointment base. Phenol in solid form is quite caustic and if present in a finely divided form in an ointment base it may cause blisters. Therefore, it must be dispensed in a suitable base which should keep the phenol in solution form. Hence, a base consisting of a mixture of hard and soft paraffins, beeswax and lard is recommended for phenol. similarly in the preparation of compound mercury ointment, olive oil is used to keep the camphor in solution form.
Emulsifying properties : Hydrocarbon bases can absorb only a small amount of water in comparison to animal fats which can absorb a large quantities of water. For example, wool fat can absorb about 50% of water, and when mixed with other fats can take up several times its own weight of water or hydro-alcoholic liquids. Hence, wool fat is included for the preparation of base meant for eye ointments. Similarly cetrimide emulsifying ointment is capable of absorbing considerable amount of water forming o/w creams.
Consistency : The ointments should be of suitable consistency. It should neither be too hard nor too soft. The consistency of an ointment base should be such, that it withstand wide variation in temperature conditions. Thus in summer, the ointment should not become too soft and in winter not too hard to be difficult to remove it from the container and spread over the skin. The consistency of an ointment can be adjusted in such a way that it contains a suitable quantity of high melting point substances like hard paraffin, beeswax etc., in soft ointments and low melting point substances like liquid paraffin in hard ointments respectively.